
NeroDigital AVC Codec

Unfortunately, Nero keeps its certification program a secret, so I cannot exactly tell you what each profile means. But, the profiles unlock more advanced features in the following order: Mobile - AVC, Portable - AVC, Standard - AVC, Cinema - AVC, HDTV - AVC and Maximum Definition - AVC. Keep in mind that more advanced profiles also mean slower encoding speed. For DVD input, Standard or Cinema are probably the most suitable profiles.
After selecting the profile, press Next to proceed.
By default, Recode wants to go directly to burning, but you'll want to configure some more first, so select Nero Digital Settings.
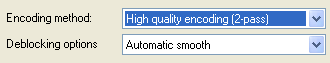
By default, Recode only allows you to configure the Encoding method, and to set the Deblocking options. Two pass encoding delivers higher quality but obviously takes longer (not quite twice as much because audio is only encoded once, and the first pass is considerably faster than the second pass). Yet you should always go for 2 pass encoding. In the Deblocking options, you can choose between smoothness and sharpness. Selecting Automatic smooth, will keep the picture smooth and tries to avoid blocks at the expense of sharpness, whereas Automatic sharp might result in a few more blocks, but also more details in the video.
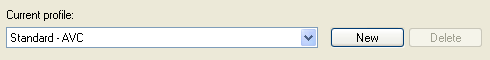
You'll note that Recode once again lists the profile you have selected. You can create your own profile by pressing New. Recode will then automatically copy the settings from the current profile to your newly created one.
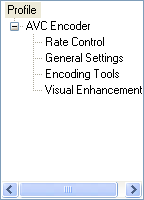
Check the Expert mode checkbox and you'll get access to the advanced settings, which are structured in a tree like structure:
Under Rate Control, you can the Encoding method again (1-pass or 2-pass).
 Using
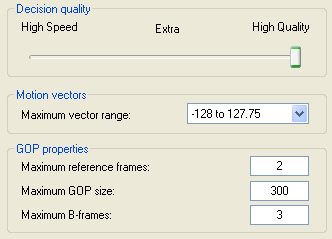
the Decision quality slider, you can configure if the encoder will spend
more time to improve quality or encode faster at the expense of quality. High
Quality obviously delivers the best quality at the expense of speed, High
Speed does the inverse.
Using
the Decision quality slider, you can configure if the encoder will spend
more time to improve quality or encode faster at the expense of quality. High
Quality obviously delivers the best quality at the expense of speed, High
Speed does the inverse.
Then you can configure the range of motion vectors using the Maximum vector range. The option decides how far an object can move between frames and still be recognized. Higher values are better but also degrade performance because a larger area of the picture has to be searched.
Maximum reference frames indicates how many previous frames can be referenced by a P-/B-frame.
The Maximum GOP size specifies the maximum distance between two I-frames (those are frames stored completely without any reference to previous frames, I-frames are usually the least compressed frames).
Finally, you can specify how many consecutive B-frames will be used by setting a value in the Maximum B-frames field.
There are more configuration options in the Encoding Tools section.
 Checking
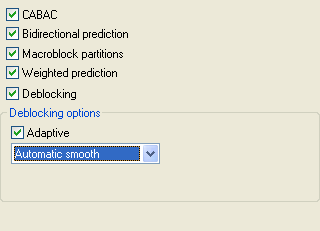
CABAC makes use of the CABAC entropy encoding in the bitstream.
Checking
CABAC makes use of the CABAC entropy encoding in the bitstream.
Bidirectional prediction enables B-frames (unchecking it disabled the use of B-frames).
Macroblock partitions enable partitioning of macroblocks. This is a tool to help with bitstream corruption.
Weighted prediction allows weighing reference frames and helps encoding scenes that fade in/out.
Deblocking enables the in-loop deblocking filter in the encoder. It's mean to prevent blocks right in the encoder. If you check Deblocking, the Deblocking options become active. You'll now have the same choice as in the easy mode between Automatic smooth and Automatic sharp. In addition, you have Deblocking strength, which activates a slider that allows you to configure the deblocking strength manually. The higher the value, the stronger the deblocking.
Finally, we have the Visual Enhancements.
 In
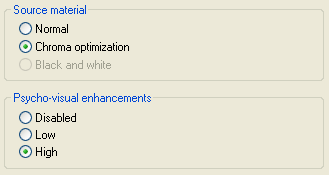
Source material, you can configure what kind of input you have. Selecting
Chroma optimization rather than Normal activates a chroma improvement
function (helps with colors). However, it can also be very useful for regular
movies. In fact, in the recent codec comparison that NeroDigital AVC won, the
cartoon mode was always activated.
In
Source material, you can configure what kind of input you have. Selecting
Chroma optimization rather than Normal activates a chroma improvement
function (helps with colors). However, it can also be very useful for regular
movies. In fact, in the recent codec comparison that NeroDigital AVC won, the
cartoon mode was always activated.
Finally, the Psycho-visual enhancements use properties of the human visual system to make the resulting image more visually pleasing to the human eye. You can disable them, use them at Low strength, or High strength.
There are a few more things to be configured, but since it's always the same regardless of whether you chose the AVC or ASP encoder, I put them on a separate page.
This document was last updated on August 13, 2005